 |
|
IN THIS ISSUE:
» Designing An Open-Source Power Inverter (Part 1): Goals And Specifications
» Raising The Plateau Level In Valley-Fill PFC Circuits Improves Efficiency
» Developing A 25-kW SiC-Based Fast DC Charger (Part 2): Solution Overview
» Focus On Magnetics:
Misconceptions In Power Magnetics
» Spotlight On Safety & Compliance:
Military- Vs. Commercial-Grade Resistors: Reliability, Performance And Cost Tradeoffs
» New Power Products
» Other Top Power News
From the Editor's Desk David G. Morrison
Editor, HOW2POWER TODAY

Open-source is not a term usually associated with power supplies, a field in which the quest for better performance leads to development of proprietary designs using highly specialized, often customized components and packaging, by highly skilled engineering teams adept in various disciplines. However, there may be times when the open-source approach could benefit power supply users. In his design article in this issue, Dennis Feucht makes the case for an open-source power inverter, which he believes could overcome the lack of serviceability of the battery-powered inverters currently on the market. In part 1 of his new series, he outlines the structure and specifications for a scalable power inverter design that he will be presenting so that engineers and others with technical knowledge may build, modify or service the design. The series will also offer the opportunity to demonstrate Dennis’ magnetics design concepts, as regularly discussed in the Focus on Magnetics column. Additionally, this newsletter offers features on a new twist on the valley-fill PFC circuit that improves efficiency in high-power designs, a solution overview for the previously introduced fast EV charger, common misconceptions in magnetics design, and a comparison of military- and commercial-grade resistors. In the latest product news, you’ll find a heavy dose of gate drivers and power modules. All this and more in the May issue.
|
|

|
HOW2POWER EXCLUSIVE DESIGN ARTICLES 
|
Designing An Open-Source Power Inverter (Part 1): Goals And Specifications
by Dennis Feucht, Innovatia Laboratories, Cayo, Belize
This is the first in a series of articles that will disclose the engineering of a kilowatt-level, scalable open-source battery inverter dubbed the “Volksinverter”—a product meant to be suitable for widespread use, and which can be built and/or serviced by technically savvy individuals. Its key characteristic is the open-source nature of this design. In this article series, the design of the Volksinverter will be described in enough detail that a technical owner will be able to maintain, repair, or even modify the design, including the magnetic components. Like Linux, the Volksinverter design will lend itself to discussion by user groups on the Internet who will be able to share ideas, observations, procedures, modifications, corrections and enhancements of it. Anyone will be free to manufacture and sell it, as-is or in modified form.
Read the article…
|
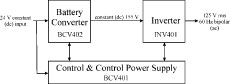
A system-level diagram of the
Volksinverter shows its three main
subsystems. |

|
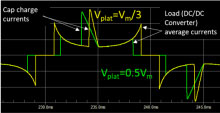
In constant-power mode, lowering
the VF plateau level to increase the
conduction angle of the rectifier has
the side effect of increasing the
current stress on the dc-dc
converter’s active components. |
Raising The Plateau Level In Valley-Fill PFC Circuits Improves Efficiency
by Viktor Vogman, Power Conversion Consulting, Olympia, Wash.
The passive capacitive PFC circuit, which employs capacitor-diode networks in the valley-fill (VF) PFC configuration, can improve power factor and reduce harmonic distortion of the input line current with a reduction in volume versus active PFC circuits. However, the operating principle of the existing VF-PFC circuit causes excessive supply voltage variations resulting in higher current magnitudes and higher power dissipation in the power conversion stages that follow the PFC stage. These losses are influenced by the so-called plateau level in the VF-PFC waveforms. This article discusses the efficiency improvement made possible by a novel implementation of the VF-PFC in which a higher than usual plateau level is employed.
Read the article…
|

Developing A 25-kW SiC-Based Fast DC Charger (Part 2): Solution Overview
by Oriol Filló, Karol Rendek, Stefan Kosterec, Daniel Pruna, Dionisis Voglitsis, Rachit Kumar and Ali Husain, ON Semiconductor, Phoenix, Ariz.
In the previous installment of this series, the authors introduced the main system requirements for a fast EV charger, outlined the key stages of the development process for such a charger and identified the team of application engineers which is developing the charger described here. Now, in part 2 they will take a closer look into the guts of the design and unveil more details of it. In particular, they’ll review the possible topologies, discuss their advantages and tradeoffs, and discuss the backbone of the system, which includes a half-bridge SiC MOSFET module.
Read the article…
|
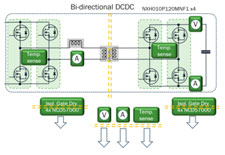
For this EV charger design, the team
selected a six-switch active rectifier
for the ac-dc stage and a dual active
bridge for the dc-dc converter stage
(shown here). |


FOCUS ON MAGNETICS 
Sponsored by Payton Planar Magnetics
A monthly column presenting information on power magnetics design, products, or related technology |

Misconceptions In Power Magnetics
by Dennis Feucht, Innovatia Laboratories, Cayo, Belize
Magnetic components appear to be so simple—just two parts, a core and some wire wrapped around it. How could that be very complicated? If you ask this question of yourself seriously enough, you begin your own descent into the abyss of magnetics design. As a “recovering magnetaholic,” I have learned that magnetics really is simple, but the path to simplicity has some misleading ideas and some that are not actually true, though they are widespread. More importantly, some basic concepts that should be widely known are not. This article is a chat about some of them.
Read the full article…
|

 |
 |

SPOTLIGHT ON SAFETY & COMPLIANCE 
A monthly column discussing standards and regulatory requirements affecting power electronics |

Military- Vs. Commercial-Grade Resistors: Reliability, Performance And Cost Tradeoffs
by Kory Schroeder, Stackpole Electronics, Raleigh, N.C.
Military-spec resistors provide an essential function in high reliability and critical circuit applications. However, unless you are dealing with such applications regularly, understanding what military-spec (military-grade) resistors offer compared to commercial resistors can be challenging. There are many aspects of military-spec resistors that are unclear or unknown to many customers. For example, a key distinction among military-spec resistors is whether or not they offer established reliability. This article explains in broad terms how military specifications address reliability in the manufacturing, testing, inspection and processing of resistors, and how these aspects compare with those used to produce commercial- and automotive-grade resistors.
Read the full article…
|

 |
 |

 |
|
|

 — POWER PRODUCTS IN 3 IMAGES OR LESS — POWER PRODUCTS IN 3 IMAGES OR LESS 
|

Pre-Switch’s CleanWave200
inverter evaluation system. |
Inverter Eval System Shows >99% Efficiency At 100 kHz Using SiC MOSFETs
 Waveforms: The Pre-Switch AI-based controller enables users to migrate from lossy, expensive hard-switching implementations to high efficiency, soft-switching designs. By virtually eliminating switching losses, the AI-based zero-voltage switching enables a host of benefits through higher frequency switching including reduced motor losses, smaller magnetics and passives, and use of discrete SiC MOSFETs (or even SiC cascodes) in place of more expensive SiC power modules. Waveforms: The Pre-Switch AI-based controller enables users to migrate from lossy, expensive hard-switching implementations to high efficiency, soft-switching designs. By virtually eliminating switching losses, the AI-based zero-voltage switching enables a host of benefits through higher frequency switching including reduced motor losses, smaller magnetics and passives, and use of discrete SiC MOSFETs (or even SiC cascodes) in place of more expensive SiC power modules.
See the full story…
|

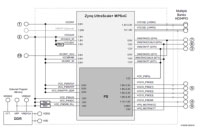
AnDAPT AmP PMICs. |
PMICs Offer Customized And Compact Power Supply Solutions For FPGAs
 Diagrams: The PMICs offer six power supply solutions for powering Xilinx Zynq UltraScale+ (ZU+) MPSoC FPGAs. The Xilinx ZU+ MPSoC power architecture requires more than 25 power rails. According to the company, AnDAPT reference designs based on the AmP PMIC meet or exceed the Xilinx power performance specifications while achieving a reduction in PCB area. Diagrams: The PMICs offer six power supply solutions for powering Xilinx Zynq UltraScale+ (ZU+) MPSoC FPGAs. The Xilinx ZU+ MPSoC power architecture requires more than 25 power rails. According to the company, AnDAPT reference designs based on the AmP PMIC meet or exceed the Xilinx power performance specifications while achieving a reduction in PCB area.
See the full story…
|




Power Integrations’ SCALE-2 gate
drivers. |
Plug-And-Play Gate Drivers Target Railway Applications
 Diagram: Mechanically ruggedized and electrically protected with comprehensive protection features to support use in railway applications, the SCALE-2 gate drivers are compact single-channel intelligent plug-and-play gate drivers optimized for 130- x 140-mm single-IGBT high power (IHM) modules with support for such modules from all major manufacturers. Diagram: Mechanically ruggedized and electrically protected with comprehensive protection features to support use in railway applications, the SCALE-2 gate drivers are compact single-channel intelligent plug-and-play gate drivers optimized for 130- x 140-mm single-IGBT high power (IHM) modules with support for such modules from all major manufacturers.
See the full story…
|



CISSOID’s Three-Phase SiC
MOSFET IPMs. |
Intelligent SiC Power Modules For E-Mobility And Aerospace Applications
 Diagrams: The CXT-PLA3SA12340A is a three-phase 1200-V, 340-A SiC MOSFET-based intelligent power module (IPM) which employs a pin-fin heatsink for liquid cooling. A 550-A rated version (the CXT-PLA3SA12550AA) is also offered. The CMT-PLA3SB12340AA is a 340-A rated air-cooled version. Diagrams: The CXT-PLA3SA12340A is a three-phase 1200-V, 340-A SiC MOSFET-based intelligent power module (IPM) which employs a pin-fin heatsink for liquid cooling. A 550-A rated version (the CXT-PLA3SA12550AA) is also offered. The CMT-PLA3SB12340AA is a 340-A rated air-cooled version.
See the full story…
|




Infineon Technologies’
EiceDRIVER X3 gate driver
families. |
Easy-To-Design-In Gate Drivers Offer Reinforced Isolation
 Photo: The EiceDRIVER X3 Compact, and X3 Enhanced Analog and Digital gate driver IC families have been expanded with variants in the three product families that feature reinforced isolation, providing power supply designers with VDE 0884-11 certified options for silicon and wide-bandgap device types up to 2300 V. Photo: The EiceDRIVER X3 Compact, and X3 Enhanced Analog and Digital gate driver IC families have been expanded with variants in the three product families that feature reinforced isolation, providing power supply designers with VDE 0884-11 certified options for silicon and wide-bandgap device types up to 2300 V.
See the full story…
|


|







|

 |
|  |

 |
|  |


 KYOCERA and AVX will establish the new "KYOCERA AVX" brand to enhance business worldwide. KYOCERA and AVX will establish the new "KYOCERA AVX" brand to enhance business worldwide.
 Radiation Test Solutions (RTS), a provider of radiation effects analysis and testing services on electronics and materials, has reached an agreement to acquire the UK-based Radtest, which developed the SEREEL2 laser system. Radiation Test Solutions (RTS), a provider of radiation effects analysis and testing services on electronics and materials, has reached an agreement to acquire the UK-based Radtest, which developed the SEREEL2 laser system.



 The AirFuel Alliance, an authority on next-gen wireless power technology and standards, has launched an automated test system and a certification program to support the AirFuel Resonant standard. The AirFuel Alliance, an authority on next-gen wireless power technology and standards, has launched an automated test system and a certification program to support the AirFuel Resonant standard.



 Navitas Semiconductor has announced its plan to go public. Navitas Semiconductor has announced its plan to go public.



ABOUT THIS NEWSLETTER: Thank you for reading HOW2POWER TODAY.
How2Power sends no more than one e-mail per month to registered users. Continuing your subscription ensures you'll receive future newsletters. Manage Your Subscription
©2020 All rights reserved. www.how2power.com
|
|