 |
|
IN THIS ISSUE:
» A Guide To Power Electronics Design For Off-Battery Automotive (Part 1): EMC And Line Transient Requirements
» Designing An Open-Source Power Inverter (Part 4): The Optimal Power-Line Waveshape
» Adjust The Output Of An Inverting Buck-Boost Regulator Without Level Shifting
» Focus On Magnetics:
Calculating Minimum Magnetic Core Size For A Transformer
» Special Guest Commentary:
Improving The Reliability Of Silicon Carbide Power Devices
» New Power Products
» Industry Events
» Other Top Power News
From the Editor's Desk David G. Morrison
Editor, HOW2POWER TODAY

The transition to electric vehicles continues to drive development of numerous power components to operate in systems with high-voltage batteries and large power converters (traction inverters, dc-dc converters and on-board chargers). You’ll see evidence of this industry focus in the product news in this and most every issue of the newsletter. At the same time, there is the concurrent trend of vehicle electrification that involves development of numerous other embedded electronic systems intended to enhance the driving experience and vehicle safety. Advanced driver assistance systems come to mind, but there are numerous other embedded applications throughout the vehicle. Naturally, these applications require dc-dc conversion to operate off of the 12-V buses in cars and the 24-V buses in heavy vehicles. A previous article series by Tim Hegarty looked extensively at what’s required to design these dc-dc converters to limit the conducted and radiated emissions produced to comply with the relevant CISPR and other international regulations. Now in a new series starting in this issue, Tim discusses details of the standards that these converters must meet to satisfy EMC requirements for conducted and radiated immunity. This time the list of standards is quite long as it includes the various requirements imposed by the different automakers. Subsequent parts of this series will address the design of converters to meet these standards, while operating from 12-V, 48-V and even 400-V/800-V buses. While there have been many articles addressing design of power converters to limit EMI generation, the subject of designing converters for immunity seems to get less attention. Yet as automotive electronic systems proliferate, and become more complex and dense, designing for immunity is likely to become challenging. More focus on this subject will be needed both to educate new designers and deal with the increasing complexities of automotive electronics.
|
|

|
HOW2POWER EXCLUSIVE DESIGN ARTICLES 
|
A Guide To Power Electronics Design For Off-Battery Automotive (Part 1): EMC And Line Transient Requirements
by Timothy Hegarty, Texas Instruments, Phoenix, Ariz.
Given the increasing number of power electronic systems integrated within vehicle designs, it is essential to consider the complicated electrical and electromagnetic environment in which these systems operate. All vehicle OEMs and most component suppliers to the OEMs perform tests to verify the electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) of their devices. In a previous 18-part series, the author discussed requirements related to conducted emissions and radiated emissions. However, there is another area of EMC that is equally important and it encompasses three types of immunity—conducted, radiated and electrostatic discharge—which you should understand before tackling an automotive power design. In part 1 of this series, the author discusses the immunity, ESD and supply-line transient requirements associated with conventional vehicle electrical systems, both 12 V and 24 V.
Read the article…
|
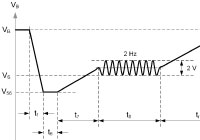
In ISO 16750-2, the level III profile for
cold crank of the 12-V system specifies
the battery voltage falling to 3 V for 15 ms—a
challenge for buck regulators. |

|
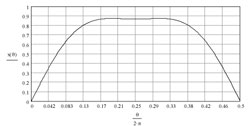
A waveshape with both sine-wave
and square-wave properties
overcomes some of the square-wave
disadvantages while reducing the
figures of demerit and noise. |
Designing An Open-Source Power Inverter (Part 4): The Optimal Power-Line Waveshape
by Dennis Feucht, Innovatia Laboratories, Cayo, Belize
What is the optimal waveshape for a power-line inverter to generate? In part 2 of this series, we began to address this question, noting the effects of inverter output waveshape on power component ratings, efficiency and its influence on the choice of the two-stage power architecture selected for this Volksinverter design. We concluded by noting that ultimately these considerations led to our selection of a third-harmonic sine wave (3HSW) for the inverter waveshape. In this part 4, we’ll delve further into why that waveshape is optimal. After comparing waveshape characteristics of sine waves, square waves and third-harmonic sine waves, we’ll look at some PWM switching techniques that can be applied to the H-bridge to generate these waveforms.
Read the article…
|

Adjust The Output Of An Inverting Buck-Boost Regulator Without Level Shifting
by Hrag Kasparian, Texas Instruments, Santa Clara, Calif. and David Baba, Texas Instruments, Phoenix, Ariz.
Switching power applications sometimes require external adjustment of the output voltage setpoint. A common way to adjust the setpoint is to use a microcontroller to generate a variable voltage through either a D-A converter or an averaged PWM signal. This is straightforward when the dc control voltage, input voltage, output voltage and regulator share the same reference—typically the system ground reference (GND). But things get interesting when trying to adjust the output of an inverting buck-boost regulator, where the output voltage is negative and the regulator GND reference is not the same as the system GND. Typically, a level-shifting circuit is required, which adds several extra components. However, under certain operating conditions, the level shifter can be eliminated and a very simple voltage-adjustment scheme can be applied.
Read the article…
|
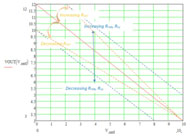
The voltage-adjustment scheme
introduced here is simple in
terms of circuitry, but calculating
its component values is not trivial. |


FOCUS ON MAGNETICS 
Sponsored by Payton Planar Magnetics
A monthly column presenting information on power magnetics design, products, or related technology |

Calculating Minimum Magnetic Core Size For A Transformer
by Gregory Mirsky, Design Engineer, Deer Park, Ill.
In inductors the load current is the core magnetizing current, while in transformers the core magnetizing current is separate from the load current. This is why in inductors (chokes) the size-defining parameter is operating power, while in transformers the magnetizing current ripple, which may constitute 0.5% to 1% of the input ac current, determines core saturation and thus the minimum size of the core. Therefore, a transformer design needs answers to more questions on what assumptions should be made to design a transformer properly. This article is going to clarify what these assumptions are, while deriving the equations needed to determine minimum core size in a power converter application.
Read the full article…
|

 |
 |

 |

|

SPECIAL GUEST COMMENTARY  |
|
Improving The Reliability Of Silicon Carbide Power Devices
by Peter Friedrichs, Infineon Technologies, Erlangen, Germany
Silicon carbide (SiC) devices offer many advantages, especially in power-conversion circuits for applications where efficiency is at a premium. These include solar inverters and electric vehicles, which may also be expected to remain in service for decades. For these applications, a combination of very high efficiency and long-term reliability is essential. The challenge in deploying SiC in such applications is that the technology is at an earlier stage of development than silicon. This means that the best ways of deploying SiC are still being explored, and that some failure modes unique to SiC devices still need to be better understood and more effectively mitigated. Infineon has been working on these issues for years and so has the insights and experience necessary to both help customers deploy SiC devices to their advantage, and to understand and mitigate their failure mechanisms to ensure the necessary reliability.
Read the full story…
|

 |

|

 |
|
|

 — POWER PRODUCTS IN 3 IMAGES OR LESS — POWER PRODUCTS IN 3 IMAGES OR LESS 
|


Advanced Energy Industries’
ALTA platform RF power delivery
solution. |
RF Power Delivery Platform For Industrial Plasma Applications
 Photo: Available with power levels from 1.5 kW to 6 kW, the ALTA series comprises 13.56-MHz rack-mounted RF power supplies and a 13.56-MHz digital tapped matching network. The power supplies and matching network provide precise, repeatable control and dynamic response in next-generation plasma processes. Photo: Available with power levels from 1.5 kW to 6 kW, the ALTA series comprises 13.56-MHz rack-mounted RF power supplies and a 13.56-MHz digital tapped matching network. The power supplies and matching network provide precise, repeatable control and dynamic response in next-generation plasma processes.
See the full story…
|

 |

|


Empower Semiconductor’s
EP71xx integrated voltage
regulators. |
Tiny, Quad-Output Regulators Need No External Inductors Or Capacitors
 Diagram: The series of 3.3-V input, digitally configurable, quad-output stepdown converters, also referred to as IVRs, are said to offer the industry’s highest power density. These devices integrate up to four integrated voltage regulators with total output up to 12 A in a 5-mm x 7-mm x 0.7-mm chipscale package. These devices provide extensive fault protection without external discrete components. Diagram: The series of 3.3-V input, digitally configurable, quad-output stepdown converters, also referred to as IVRs, are said to offer the industry’s highest power density. These devices integrate up to four integrated voltage regulators with total output up to 12 A in a 5-mm x 7-mm x 0.7-mm chipscale package. These devices provide extensive fault protection without external discrete components.
See the full story…
|

 |

|

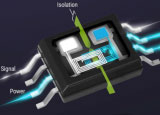
Texas Instruments’ TPSI3050-Q1
isolated switch driver and
TPSI2140-Q1 1isolated switch. |
SSRs Shrink Design Size, Improve Reliability And Safety In 800-V EVs
 Photo: The portfolio of solid-state relays includes automotive-qualified isolated drivers and switches that are said to deliver industry-leading reliability to help make electric vehicles (EVs) safer. The isolated solid-state relays (SSRs) also provide the smallest solution size while reducing the bill-of-materials cost of powertrain and 800-V battery-management systems, according to the vendor. Photo: The portfolio of solid-state relays includes automotive-qualified isolated drivers and switches that are said to deliver industry-leading reliability to help make electric vehicles (EVs) safer. The isolated solid-state relays (SSRs) also provide the smallest solution size while reducing the bill-of-materials cost of powertrain and 800-V battery-management systems, according to the vendor.
See the full story…
|


Efficient Power Conversion’s
EPC2050 350-V GaN transistor. |
350-V GaN Transistor Boasts Small Size And Low Cost
 Photo: This 350-V, 80-mΩ max. RDS(ON) power transistor comes in a 1.95-mm x 1.95-mm chip-scale package. It’s well suited for use in multi-level converters, EV charging, solar power inverters, lidar, and LED lighting. Photo: This 350-V, 80-mΩ max. RDS(ON) power transistor comes in a 1.95-mm x 1.95-mm chip-scale package. It’s well suited for use in multi-level converters, EV charging, solar power inverters, lidar, and LED lighting.
See the full story…
|

|







|

 |
|  |

INDUSTRY EVENTS  |
|
Experts On Power Packaging To Gather At IWIPP 2022 In Grenoble
Registration is now open for IWIPP 2022, a PSMA and IEEE sponsored hybrid workshop, which will be held August 24-26, 2022, at the World Trade Center in Grenoble, France, and hosted by G2E Labs. IWIPP is a growing and successful power technology workshop with excellent speakers and networking opportunities. Under the leadership of general chairman Francesco Iannuzzo, professor, Aalborg University, IWIPP brings together industry, academic and government researchers in the field of power electronics components, electrical insulating materials, and packaging technologies to facilitate and promote the development and commercialization of high-density and high-efficiency power converters.
Read the full story…
|
|
PCIM Asia 2022 To Highlight Electrification Of Transportation Systems
Established in 2002, PCIM Asia is the only specialized exhibition and conference platform in China for power electronics, intelligent motion, renewable energy, and energy management in the Asian market. This year’s edition of PCIM Asia, which will be held August 31 through September 2, 2022 in Shanghai, will highlight the topic “Electrification of Transportation Systems.”
Read the full story…
|

 |
|  |


 The DOE has announced $5 million to launch a lithium-battery workforce initiative. The DOE has announced $5 million to launch a lithium-battery workforce initiative.
 Odyssey Semiconductor Technologies has reached a technology milestone in developing what it describes as the world's most advanced vertical GaN power FETs. Odyssey Semiconductor Technologies has reached a technology milestone in developing what it describes as the world's most advanced vertical GaN power FETs.



 Energous, a developer of RF-based wireless power networks, has announced that its 1-W WattUp PowerBridge transmitter technology has been approved by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology in China for IoT applications. Energous, a developer of RF-based wireless power networks, has announced that its 1-W WattUp PowerBridge transmitter technology has been approved by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology in China for IoT applications.
 ROHM Semiconductor is partnering with Delta Electronics to develop GaN power devices. ROHM Semiconductor is partnering with Delta Electronics to develop GaN power devices.



 Winners of APEC 2022’s technical session awards are now posted online. Winners of APEC 2022’s technical session awards are now posted online.
 According to a report by Future Market Insights, the global dc power supplies market is expected to reach $447.33 million by 2025, up from $378 million in 2021. According to a report by Future Market Insights, the global dc power supplies market is expected to reach $447.33 million by 2025, up from $378 million in 2021.

ABOUT THIS NEWSLETTER: Thank you for reading HOW2POWER TODAY.
How2Power sends no more than one e-mail per month to registered users. Continuing your subscription ensures you'll receive future newsletters. Manage Your Subscription
©2020 All rights reserved. www.how2power.com
|
|